Recommendation for individuals using a screenreader: please set your punctuation settings to "most."
Descriptive Statements:
- Select an appropriate word (e.g., verb form, adjective form, pronoun) or phrase to complete a sentence.
- Select an appropriate clause or construction to complete a sentence.
- Apply principles of agreement (e.g., subject and verb, noun and adjective, pronoun and antecedent) in a passage.
- Select the correct transformation of a sentence based on given instructions (e.g., transform the tense or mood of a sentence, transform a sentence from indirect to direct statement).
- Combine two or more sentences into a single sentence that preserves the meaning of the original sentences (e.g., expressing a temporal or causal relationship between sentences through use of a subordinate clause).
- Compare and contrast features of Latin and English grammar and usage.
Sample Item:
Select the response that correctly combines the two sentences below into one sentence that preserves the meaning of the original sentences.
Fīlia in hortō clāmat. Pater fīliam audit.
- Pater quī fīliam audit in hortō clāmat.
- Pater fīliam in hortō sē audīre clāmat.
- Pater fīliam audit quae in hortō clāmat.
- Pater fīliam in hortō sē audīvisse clāmat.
Correct Response and Explanation (Show Correct ResponseHide Correct Response)
C.
Descriptive Statements:
- Identify Greek inflected forms used in Latin.
- Identify Greek loan words (e.g., peristylium, philosophia).
- Select an accurate transliteration of a Greek word or phrase in context (e.g., from the first book of Homer's Iliad or Plato's Apology).
Sample Item:
Use the sentence below from Homer's Iliad to answer the question that follows.
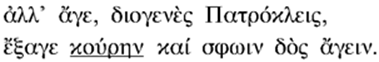
Spelling for the underlined word in a sentence, kappa omicron upsilon rho eta nu
Which of the following is the accurate transliteration of the underlined word?
- kouphey
- kourev
- kouren
- kouphen
Correct Response and Explanation (Show Correct ResponseHide Correct Response)
C.
Descriptive Statements:
- Understand the ways in which a student's primary language(s) can affect the acquisition of Latin.
- Understand the ways in which learning styles affect the acquisition of Latin.
- Understand ways in which learning challenges affect the acquisition of Latin.
- Demonstrate knowledge of how theories of language acquisition are reflected in current Latin teaching methods and materials.
Sample Item:
A Latin teacher introduces a new reading passage about the Roman baths by having students view and discuss pictures of Roman baths, watch a video tour of a Roman bath, and attach new vocabulary words to a model of a Roman bath. Through these prereading activities, the teacher is primarily demonstrating the importance of supporting students' reading comprehension by:
- providing students with opportunities to approach a text using a variety of learning styles.
- establishing clear expectations for what students will know and be able to do once they have read a text.
- allowing students the chance to draw connections between a text and its author.
- modeling strategies students can use to monitor their own comprehension of the content of a text.
Correct Response and Explanation (Show Correct ResponseHide Correct Response)
A.

